PRIVACY-PRESERVING
MULTI-KEYWORD RANKED SEARCH OVER ENCRYPTED CLOUD DATA
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE OUTPUT
CLICK HERE TO VIEW THE OUTPUT
ABSTRACT:
With the advent of cloud
computing, data owners are motivated to outsource their complex data management
systems from local sites to the commercial public cloud for great flexibility
and economic savings. But for protecting data privacy, sensitive data have to be
encrypted before outsourcing, which obsoletes traditional data utilization
based on plaintext keyword search. Thus, enabling an encrypted cloud data
search service is of paramount importance. Considering the large number of data
users and documents in the cloud, it is necessary to allow multiple keywords in
the search request and return documents in the order of their relevance to
these keywords. Related works on searchable encryption focus on single keyword
search or Boolean keyword search, and rarely sort the search results. In this
paper, for the first time, we define and solve the challenging problem of
privacy-preserving multi keyword ranked search over encrypted data in cloud
computing (MRSE). We establish a set of strict privacy requirements for such a
secure cloud data utilization system. Among various multi-keyword semantics, we
choose the efficient similarity measure of “coordinate matching,” i.e., as many
matches as possible, to capture the relevance of data documents to the search
query. We further use “inner product similarity” to quantitatively evaluate
such similarity measure. We first propose a basic idea for the MRSE based on
secure inner product computation, and then give two significantly improved MRSE
schemes to achieve various stringent privacy requirements in two different
threat models. To improve search experience of the data search service, we
further extend these two schemes to support more search semantics. Thorough
analysis investigating privacy and efficiency guarantees of proposed schemes is
given. Experiments on the real-world data set further show proposed schemes
indeed introduce low overhead on computation and communication.
EXISTING SYSTEM:
To meet the effective data
retrieval need, the large amount of documents demand the cloud server to
perform result relevance ranking, instead of returning undifferentiated
results. Such ranked search system enables data users to find the most relevant
information quickly, rather than burdensomely sorting through every match in
the content collection [5]. Ranked search can also elegantly eliminate
unnecessary network traffic by sending back only the most relevant data, which is
highly desirable in the “pay-as-you-use” cloud paradigm. For privacy
protection, such ranking operation, however, should not leak any keyword
related information. On the other hand, to improve the search result accuracy
as well as to enhance the user searching experience, it is also necessary for
such ranking system to support multiple keywords search, as single keyword
search often yields far too coarse results. As a common practice indicated by today’s
web search engines (e.g., Google search), data users may tend to provide a set
of keywords instead of only one as the indicator of their search interest to
retrieve the most relevant data. And each keyword in the search request is able
to help narrow down the search result further. “Coordinate matching” [6], i.e.,
as many matches as possible, is an efficient similarity measure among such multi-keyword
semantics to refine the result relevance, and has been widely used in the
plaintext information retrieval (IR) community. However, how to apply it in the
encrypted cloud data search system remains a very challenging task because of
inherent security and privacy obstacles, including various strict requirements
like the data privacy, the index privacy, the keyword privacy, and many others.
DISADVANTAGES OF
EXISTING SYSTEM:
·
It still not adequate to provide users
with acceptable result ranking functionality.
· It cannot accommodate such high service-level
requirements like system usability, user searching experience, and easy
information discovery.
· Shared data will not be secure.
PROPOSED SYSTEM:
In this paper, for the first time, we define and
solve the problem of multi-keyword ranked search over encrypted cloud data
(MRSE) while preserving strict systemwise privacy in the cloud computing
paradigm. Among various multi-keyword semantics, we choose the efficient
similarity measure of “coordinate matching,” i.e., as many matches as possible,
to capture the relevance of data documents to the search query. Specifically,
we use “inner product similarity”, i.e., the number of query keywords appearing
in a document, to quantitatively evaluate such similarity measure of that
document to the search query. During the index construction, each document is
associated with a binary vector as a subindex where each bit represents whether
corresponding keyword is contained in the document. The search query is also
described as a binary vector where each bit means whether corresponding keyword
appears
in
this search request, so the similarity
could be exactly measured by the inner product of the query vector with the
data vector. However, directly outsourcing the data vector or the query vector
will violate the index privacy or the search privacy. To meet the challenge of
supporting such multikeyword semantic without privacy breaches, we propose a
basic idea for the MRSE using secure inner product computation, which is
adapted from a secure k-nearest neighbor (kNN) technique, and then give two
significantly improved MRSE schemes in a step-by-step manner to achieve various
stringent privacy requirements in two threat models with increased attack
capabilities.
ADVANTAGES OF PROPOSED
SYSTEM:
·
It proposed schemes indeed introduce low
overhead on computation and communication.
·
It uses ranked search mechanism to
support more search semantics and dynamic data operations.
· It is more secure and efficient.
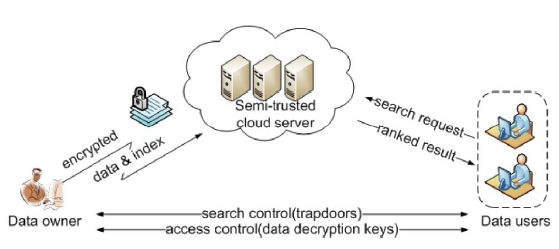
SYSTEM
ARCHITECTURE:
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION:-
HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS:-
ü Processor - Pentium –IV
ü Speed - 1.1 Ghz
ü RAM - 512 MB(min)
ü Hard
Disk - 40 GB
ü Key
Board - Standard Windows Keyboard
ü Mouse - Two or Three Button Mouse
ü Monitor - LCD/LED
SOFTWARE
REQUIREMENTS:
•
Operating system : Windows XP
•
Coding Language : Java
•
Data Base : MySQL
•
Tool : Net Beans IDE
REFERENCE:
Ning Cao, Cong Wang, Ming Li, Kui Ren and Wenjing
Lou, “Privacy-Preserving
Multi-Keyword Ranked Search over Encrypted Cloud Data” IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON
PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS, VOL. 25, NO. 1, JANUARY 2014.